When Is Diaphragm Surgery Needed?
The diaphragm is our muscle that separates the thoracic cavity, where the lungs and heart are located, from the abdominal cavity and is the most important for normal breathing.
Diaphragmatic Tear, Diaphragm Paralysis, Diaphragmatic Hernia
When hernia, paralysis, elevation, traumatic rupture or tumor occur in this muscle, it may need to be treated surgically.
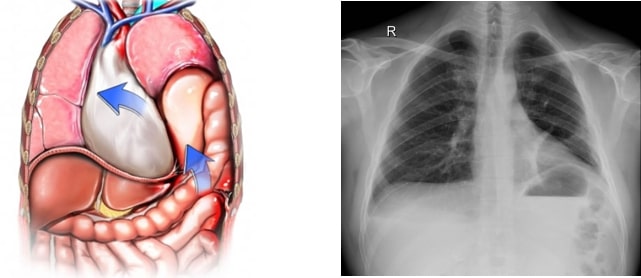
The following figure shows herniation of the stomach and intestines towards the chest cavity on the left side. In this case, in addition to shortness of breath, complaints of the gastrointestinal system (such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain) occur. If such hernias are not surgically corrected, gangrene may occur in the stomach and intestines.
What are the symptoms that occur in patients with diaphragmatic paralysis?

The most common symptom is the patient’s shortness of breath and heart palpitations while walking, climbing stairs, running or any other effort.This situation usually starts suddenly. The patient states that he has never had this type of complaint before.
In patients who apply for cardiac examination with these complaints, it is detected that the diaphragm is pushed to the other side by the rising diaphragm in the heart. One diaphragm is found to be higher than the other on chest X-ray.
How to understand that there is paralysis in the diaphragm?
The most important way to understand this is to take a film with the method called FLOROSCOPY to see if both diaphragms work during breathing.
What are the symptoms that occur in patients with diaphragmatic hernia?
Pain in the upper abdomen, nausea, postprandial indigestion, nausea and vomiting may occur as a result of the organs in the abdomen protruding upwards from a ruptured diaphragm into the chest cavity (herniation). Gangrene may occur with the compression of the stomach or intestine in the hernia. In this case, the patient develops severe pain, nausea and vomiting.
Why Do I Need to Have Diaphragm Surgery?
Since drug treatments are not sufficient in diaphragmatic diseases, surgery is required to eliminate the disease.
If a diaphragm cannot function as a result of paralysis, it is not possible for the patient to breathe normally. As a result, the patient experiences an increase in heart rate and shortness of breath (a feeling of congestion) during exertion. It is not possible for this situation to improve spontaneously or with any medication.
The operation ensures that the non-operating diaphragm muscle is stretched and lowered to where it should be. In this case, the patient’s complaints disappear.
What are the Diaphragm Surgery Methods?
The diaphragm can be accessed by opening the abdominal or chest cavity. The method of intervention is decided by evaluating factors such as the condition of the disease, whether it is on the right or left side, and the time elapsed since the onset of the disease. In addition, many diaphragm operations can be performed by endoscopic methods.
What are the Risks of Diaphragm Surgery?
The risk situation during the surgical operation varies according to the age, general condition of the patient, and whether there is an additional disease. It usually has a low complication rate. However, rare conditions such as bleeding, infection and recurrence of hernia may occur.
How long is the hospital stay after surgery?
The average hospital stay after surgery is 3-4 days.