What is Bronchiectasis?
Bronchiectasis is the permanent enlargement of the bronchi as a result of damage to the airways (bronchus) in the lung.
What Causes Bronchiectasis?
- Usually, bronchial damage occurs due to childhood infections (such as measles and pertussis).
- Past tuberculosis (tuberculosis)
- Immune system disorders (hypogammagolobulinemia)
- Congenital bronchial disorders (such as Kartogenar syndrome)
- Cystic fibrosis
- Foreign objects (nuts, peanuts, eraser tips, pins, etc.) escaping into the windpipe
- Some rare benign bronchial tumors (such as carcinoid tumors) may also cause bronchiectasis.
- In many patients, no obvious cause can be found.
What are the Symptoms that Occur in Patients with Bronchiectasis?
- cough
- producing copious amounts of phlegm
- frequent respiratory infections
- weakness
- slimming
- shortness of breath
- bad breath
- developmental delay in children
How Is Bronchiectasis Diagnosed?
- The diagnosis of bronchiectasis is usually made by the patient’s complaints and examination findings.
- Complaints of frequent respiratory tract infections and profuse sputum production are quite evident.
- Normal chest radiographs are not sufficient diagnostic tools.
- High resolution Computed Tomography is the most important diagnostic tool in the diagnosis of bronchiectasis.
- Bronchoscopy is not necessary in every patient.
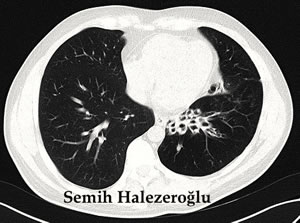
How is Bronchiectasis Treated?
- It is primarily treated with antibiotics and breathing drugs.
- Bronchial cleansing is achieved by applying the method of postural drainage (preferably in the morning, to ensure that patients cough up their sputum in certain positions)
- With respiratory physiotherapy, the lungs are strengthened and their capacity is increased.
- If there is no response to the treatment, surgery is performed
- Lung transplantation is necessary if both lungs are severely ill
In Which Situation Is Bronchiectasis Surgery Necessary?
- If it is not possible to be treated with drugs
- If the patient’s quality of life deteriorates
- In case of coughing up blood from the mouth
- If there is inflammation in the lung cavity
- If frequent hospitalization is required
What are the Bronchiectasis Surgery Methods?
Open surgery (thoracotomy) performed by opening between the ribs has left its place to the closed (VATS-Thoracoscopy) method.
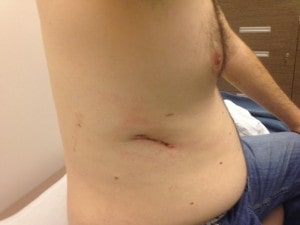
The surgical method to be preferred in bronchiectasis is closed surgery called ONE PORT VATS.
Bronchiectasis surgery is performed to improve the quality of life. For this reason, closed surgery method is preferred.
Closed Surgery in Bronchiectasis (Single Port VATS)
In this method, an incision of 3 or 4 cm is made, from which a camera and additional surgical instruments are advanced. The diseased lung lobe is removed without expanding the ribs.
The operation takes approximately 2 hours. Patients are discharged within 3 or 4 days.
As post-surgery pain is much less, returning to normal life is significantly faster than open surgery.
What are the Risks of Bronchiectasis Surgery?
There are risks such as post-surgery bleeding, pneumonia, infection, and air leakage from the lungs. These conditions can be seen in 5-7% of patients.
How Many Days Should I Stay in the Hospital After Surgery?
Patients with closed operations on average are discharged after 3-4 days.
Our Bronchiectasis Surgery is in the USA
Selected as One of the Most Creative and Educational Operations of 2014.