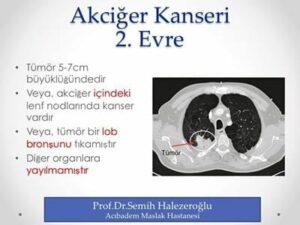
Stage 2 in lung cancer is seen in cases where the diameter of the cancer is between 5-7 cm, spread to the lymph nodes in the lung or when the tumor obstructs the bronchus.

Symptoms in Second Stage Lung Cancer
The vast majority of patients do not have obvious complaints. Cough, bloody sputum, recurrent pneumonia or other respiratory tract infections may be seen at this stage because the tumor causes obstruction in the trachea. In addition, weakness not directly related to cancer, pain in some parts of the body or swelling in the feet may be seen.
Diagnosis
Lung cancer should be considered in many complaints that occur in patients over the age of 50 and have a history of smoking. Plain lung films do not provide enough information. For this reason, low-dose scanning computed tomography is taken. If a suspicious lesion is seen here, further investigations (such as PET-CT, bronchoscopy or needle biopsy) should be performed.
Treatment in Second Stage Lung Cancer
The second stage treatment method in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancers is surgical removal of the cancerous lobe.
- first of all, closed-endoscopic method (VATS) should be preferred.
- The majority of patients also require chemotherapy after surgery.
- Radiotherapy is rarely required.
- They can be discharged after an average of 4 or 5 days in the hospital after surgery.
- They can do all their activities within 2 weeks after the surgery.
- The decision for post-operative treatment is determined by the tumor board, taking into account the pathology examination and other characteristics of the patient.
- Small Cell Lung Cancers are not operated in the second stage. Appropriate treatment in this cell type is chemotherapy and radiotherapy.